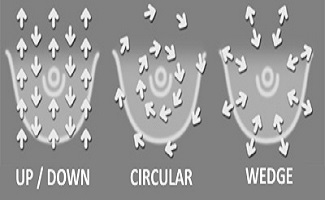
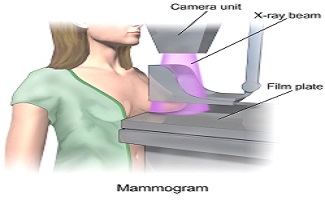
2. Cervical Cancer Screening :
Cervical screening is a way of preventing cancer by finding and
treating early changes in the neck of the womb (cervix). These
changes could lead to cancer if left untreated. The screening uses
a test called cytology, which many people know as the smear
test.
A nurse or doctor takes a sample of cells from the cervix with a
small brush. They send the sample to a laboratory to be checked
for abnormalities. In some cases, samples are also tested for a
virus called human papilloma virus (HPV) that increases the risk
of cervical cancer.
There are two types of tests used for cervical cancer screening as
:
1. Pap Test :
The Pap test can find early cell changes and treat them before
they become cancer. The Pap test can also find cervical cancer
early, when it’s easier to treat. The pap test, known earlier as
Pap smear, cervical smear, or smear test is a method of cervical
screening used to detect potentially pre-cancerous and cancerous
processes in the endocervical canal (transformation zone) of the
female reproductive system.
A Pap smear is performed by opening the vaginal canal with a
speculum, then collecting cells from the outer opening of the
cervix of the uterus and the endocervix. The cells are examined
under a microscope to look for abnormalities. The test aims to
detect potentially pre-cancerous changes (called cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical dysplasia), which are
caused by sexually transmitted human papillomaviruses. The test
remains an effective, widely used method for early detection of
pre-cancer and cervical cancer. The test may also detect
infections and abnormalities in the endocervix and endometrium.
2. HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) Test :
The HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) test finds certain infections that
can lead to cell changes and cancer. HPV infections are very
common, and most go away by themselves and don’t cause these
problems. The HPV test may be used along with a Pap test,
or to help doctors decide how to treat women who have an abnormal
Pap test. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test detects the presence
of human papillomavirus, a virus that can lead to the development
of genital warts, abnormal cervical cells or cervical cancer.
Your doctor might recommend the HPV test if:
-
Your Pap test was abnormal, showing a typical squamous cells of
undetermined significance (ASCUS)
- You’re age 30 or older
The HPV test is available only to women; no HPV test yet exists
to detect the virus in men. However, men can be infected with
HPV and pass the virus along to their sex partners.