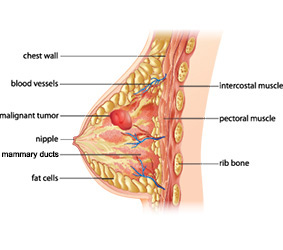
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women, after skin cancer. It is also the second leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer. Breast cancer is a disease that occurs when cells in breast tissue change (or mutate) and keep reproducing. These abnormal cells usually cluster together to form a tumor. A tumor is cancerous (or malignant) when these abnormal cells invade other parts of the breast or when they spread (or metastasize) to other areas of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, a network of vessels and nodes in the body that plays a role in fighting infection.
Causes
Breast cancer is caused by a genetic mutation in the DNA of breast cancer cells. Some mutations may develop randomly over time, while others are inherited or may be the result of environmental exposures or lifestyle factors.
Breast Cancer Symptoms
if you find an area of thickening breast tissue, a lump in your breast (usually painless, but not always) or an enlarged underarm lymph node, see your physician.
You may notice a change in the shape or size of your breast. You could have an area of skin that dimples or a nipple that leaks fluid.
Often, there are no early warning signs of breast cancer. Even if you develop a lump, it may be too small to feel. That’s why breast cancer screening, typically using mammography, is so important.
Screening
A screening mammogram (a type of breast X-ray) can identify the presence of cancer, often before symptoms arise. Women at high risk for breast cancer may also be screened with other imaging tests, like a breast MRI.
Diagnosis
An abnormal finding on a screening mammogram or discovering a lump or other breast changes doesn’t necessarily mean you have breast cancer.
Your doctor will need to perform follow-up testing using one or more types of scans. A diagnostic mammogram, which involves more X-rays than a screening mammogram, can offer a more detailed view of the area of concern. Two other tests, a breast MRI or breast ultrasound, may be ordered to gather additional diagnostic information.
There is only one way to confirm a cancer diagnosis. You will need a biopsy to extract cells or tissue from the area of the breast that is causing concern. A fine needle may be used to remove cells or tissue, or you may undergo a surgical procedure to remove a piece of breast tissue.
Dr. Vinod Gore is a well-known ONCOLOGIST and CANCER SURGEON from Pune, India. He has been trained at Tata Memorial Cancer Centre Mumbai and has experience of more than 10 years in the field of Oncology.
Presently he is working as a consultant Cancer Surgeon at all prime institutes at Pune like Sahyadri Hospital, RUBY Hall Clinic, Noble Hospital, and Inamdar Hospital. Dr. Vinod Gore is an experienced breast surgeon in Wakad, Baner, PCMC, Pune.


